If you are a business owner or a Payroll practitioner in Singapore, you will need to issue out payslips and you will also likely need to analyse yearly and monthly payroll reports, so you can make better decisions moving forward.
In this article, I will share all you need to know about the most common types of Payroll Reports in Singapore.
What Is A Payroll Report?
A payroll report is a detailed document that provides a summary of various financial aspects related to employee compensation within a specific period. It typically includes information such as:
- Employee Earnings: Breakdown of salaries, wages, bonuses, and other forms of compensation.
- Deductions: Details of deductions such as taxes, social security contributions, health insurance, and other withholdings.
- Overtime: If applicable, a report on overtime hours worked and corresponding pay.
- Leave Balances: Information on accrued and utilized leave entitlements for each employee.
- Tax Contributions: Summary of employer and employee contributions to taxes, such as income tax and social security.
- Net Pay: The final amount an employee receives after all deductions.
- Year-to-Date Totals: Cumulative figures from the beginning of the fiscal year or an employee’s tenure. These reports help businesses manage their payroll processes, ensure compliance with regulations, and maintain accurate financial records.
What are the benefits of a Payroll Report?
Payroll reports can offer several benefits to businesses:
- Compliance: Ensures adherence to local labor laws and tax regulations, avoiding legal issues.
- Accurate Financial Records: Provides a detailed breakdown of employee earnings, taxes, and deductions, aiding in accurate financial reporting.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Enables businesses to forecast labor costs, plan budgets, and allocate resources more effectively.
- Employee Transparency: Enhances transparency by clearly outlining how compensation is calculated, fostering trust among employees.
- Tax Reporting: Facilitates timely and accurate submission of tax-related documents, reducing the risk of penalties.
- Audit Trail: Creates a comprehensive audit trail, helping in case of audits or internal reviews.
- Decision-Making: Informs strategic decisions related to workforce management, compensation structures, and benefits planning. Overall, payroll reports are crucial for maintaining financial accuracy, legal compliance, and informed decision-making within a business.
What are some common payroll reports in Singapore?
Common payroll reports in Singapore include the Monthly Payroll Register, Year-to-date Payroll Register Report, Itemised Payslip, and the CPF (Central Provident Fund) Contribution Report for mandatory savings.
Employers often generate the IR8A form for annual income reporting to the tax authorities.
In the next section, I will share more about each of the 5 reports mentioned below and how they can benefit your business.
-
Year-to-date Payroll Register Report
-
Monthly Payroll Summary Report
-
Itemised Payslip
-
IR8A Form for Annual Income Reporting
-
CPF (Central Provident Fund) Contribution Report
1. Year-to-date Payroll Register Report
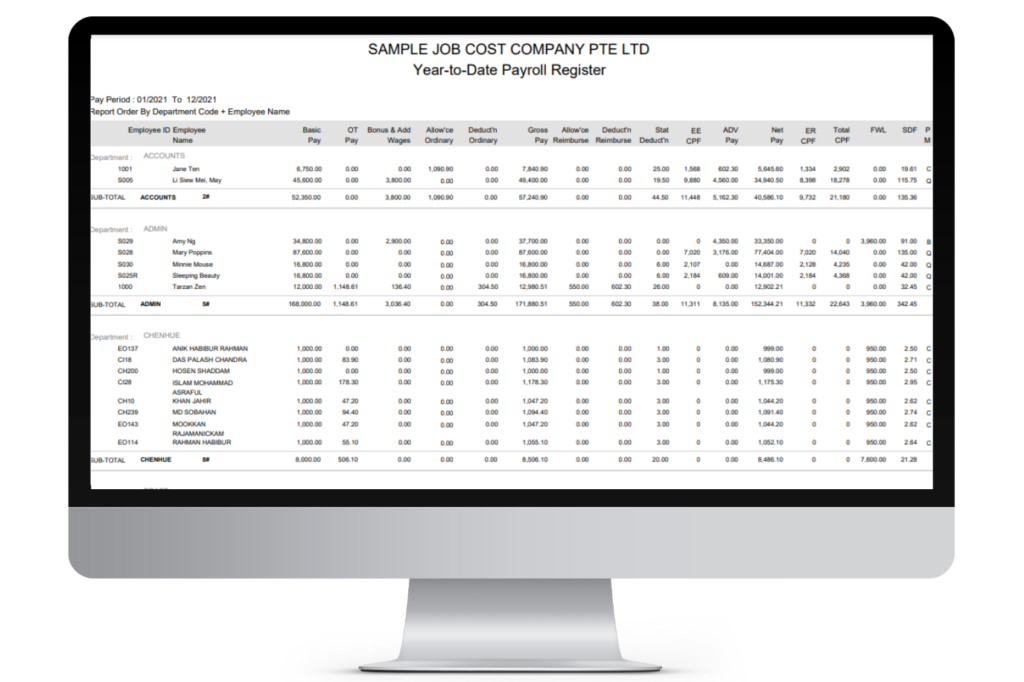
A Year-to-Date (YTD) Payroll Register Report in Singapore summarizes all payroll transactions for employees from the beginning of the calendar year until the current date. It typically includes details such as employee names, identification numbers, earnings, deductions, and net pay. This report provides a comprehensive overview of the financial aspects of payroll for a specific time frame.
2. Monthly Payroll Summary Report
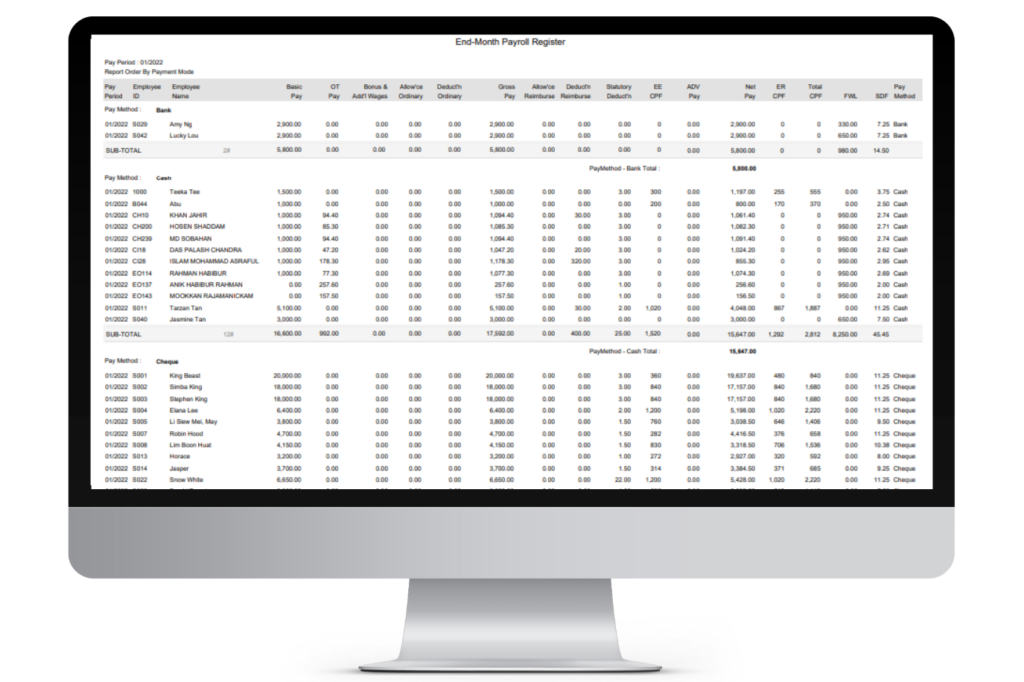
A Monthly Payroll Summary Report is a document that provides a condensed overview of payroll activities for a specific month. It typically includes key information such as:
- Employee Details: Names, identification numbers, and relevant personal information.
- Earnings: Breakdown of gross salary, bonuses, overtime, or any additional income.
- Deductions: Details of taxes, social security contributions, insurance, and other withholdings.
- Net Pay: The final amount paid to each employee after deductions.
- Employer Contributions: Contributions made by the employer, such as provident fund or retirement plan contributions.
- Total Costs: The overall cost to the employer, considering both employee earnings and employer contributions.
This report serves as a snapshot of the financial aspects of payroll for a specific month, aiding in financial planning, budgeting, and compliance.
3. Itemised Payslip In Singapore
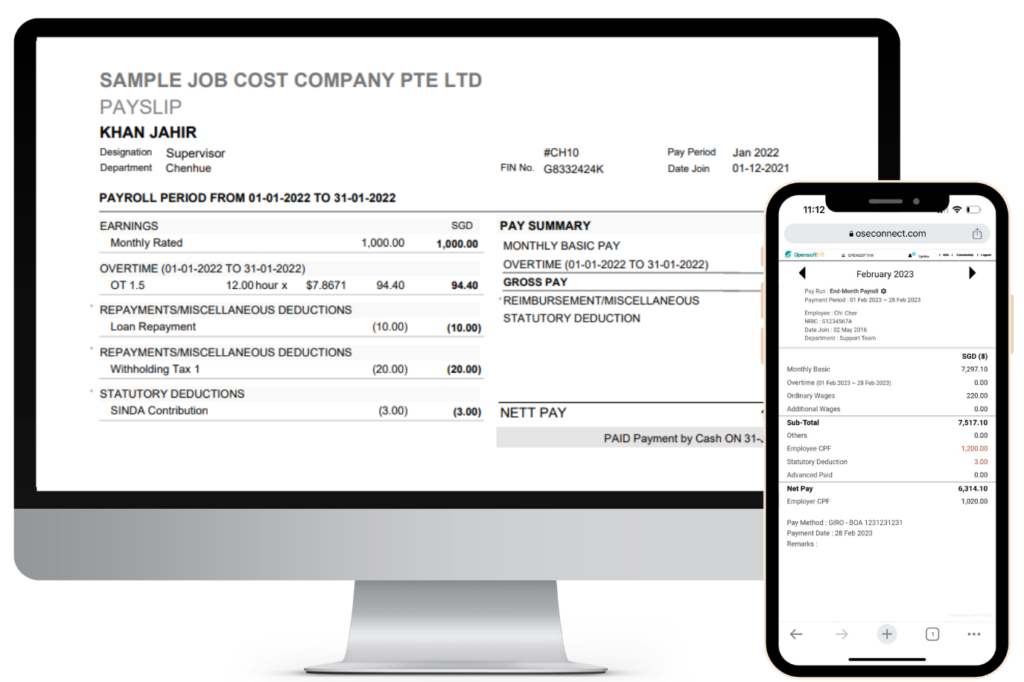
In Singapore, an itemised payslip is a document provided by employers to their employees detailing the breakdown of their salary and related financial transactions. It typically consists of the following components:
- Employee Information: Name, identification number, and other relevant personal details.
- Pay Period: Specifies the time frame for which the salary is calculated.
- Basic Salary: The fixed amount agreed upon as the regular compensation.
- Allowances: Any additional payments such as housing or transport allowances.
- Overtime Pay: If applicable, details of overtime hours worked and corresponding pay.
- Deductions: Breakdown of deductions, including taxes, social security contributions, and other withholdings.
- Net Pay: The final amount the employee receives after all deductions.
- CPF Contributions: Central Provident Fund contributions by both the employer and employee.
- Employer Contributions: Contributions made by the employer for benefits like insurance or provident fund.
- Other Relevant Information: Any other information or notes deemed important, such as leave balances or bonuses.
Itemised payslips are crucial for transparency and compliance with employment regulations in Singapore, ensuring that employees understand how their salary is calculated and what deductions are being made.
Find out more about what you need to note for itemised payslip in Singapore.
4. IR8A Form for Annual Income Reporting
The IR8A form in Singapore is an annual statement of income provided by employers to their employees. It is an essential part of the income reporting process and is used for tax purposes. The IR8A form reports various types of income and benefits received by an employee during the tax year. Here are the key components typically included on the IR8A form:
- Employer Information: Details of the employer, including name and tax reference number.
- Employee Information: Employee’s name, identification number, and other relevant details.
- Income Details:
- Basic Salary: The regular fixed salary agreed upon by the employer and employee.
- Bonuses: Any additional payments made as bonuses or incentives.
- Overtime Pay: If applicable, details of overtime hours worked and corresponding pay.
- Allowances: Various allowances such as housing, transport, or meal allowances.
- Benefits-in-kind: The cash value of non-cash benefits provided to the employee, such as accommodation or stock options.
- Employer’s CPF Contributions: Contributions made by the employer to the employee’s Central Provident Fund (CPF) accounts.
- Other Remuneration: Any other forms of remuneration or benefits provided to the employee.
Employees use the information on the IR8A form to complete their income tax returns accurately. It is crucial for employers to provide this form to their employees by March 1st of each year, allowing sufficient time for tax filing before the tax deadline in Singapore.
5. CPF (Central Provident Fund) Contribution Report
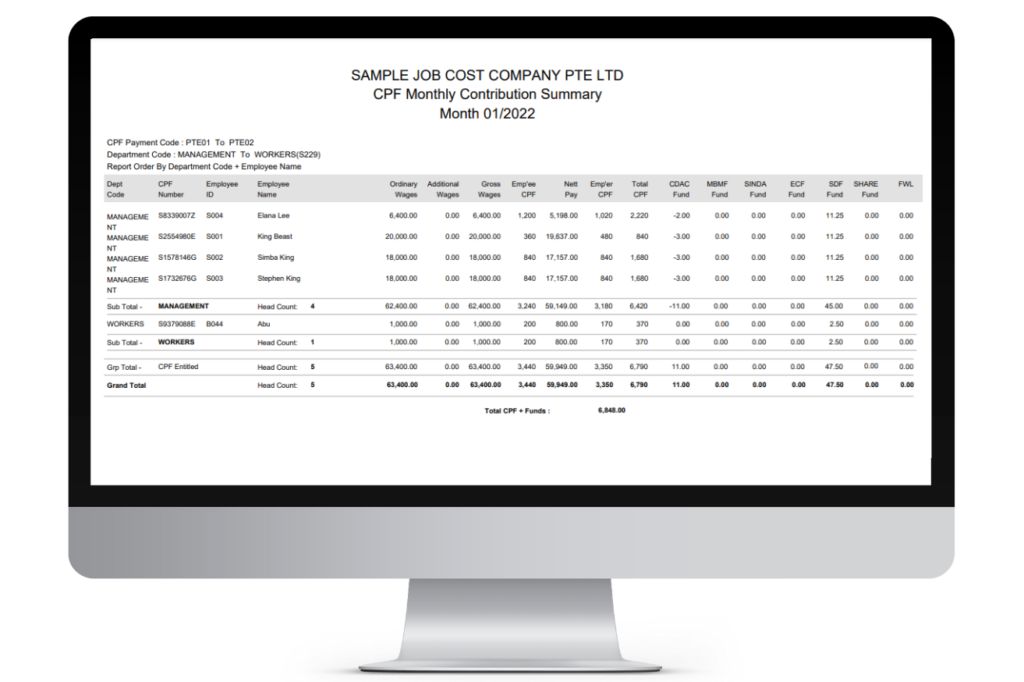
A CPF (Central Provident Fund) Contribution Report in Singapore is a document that outlines the details of CPF contributions made by both the employer and the employee. It typically consists of the following components:
- Employee Information: Name, identification number, and other relevant personal details.
- CPF Contribution Period: Specifies the timeframe for which the CPF contributions are calculated.
- Employee’s CPF Contribution: Breakdown of the employee’s share of CPF contributions, including the Ordinary Account (OA), Special Account (SA), and MediSave Account (MA).
- Employer’s CPF Contribution: Details of the employer’s contributions to the employee’s CPF accounts.
- Total CPF Contributions: The sum of both the employee’s and employer’s contributions.
- CPF Contribution Rates: Specifies the applicable CPF contribution rates for each account.
- Additional Contributions: Any additional contributions, such as voluntary or supplementary contributions.
This report is essential for both employers and employees to ensure compliance with CPF regulations and provides a clear record of the funds allocated to the employee’s CPF accounts. CPF contributions play a significant role in Singapore’s social security system, covering areas like retirement savings, healthcare, and housing.
How do you present a payroll report to your management?
Here’s a common approach on how Human Resources (HR) professionals can present payroll reports to their boss in a clear and concise manner.
- Executive Summary: Begin with a brief executive summary highlighting key points, such as total payroll expenses, any notable changes, or compliance updates.
- Visual Representation: Use charts or graphs to visually represent significant trends or variations in the payroll data. This can make complex information more digestible.
- Comparisons: Provide comparisons to previous periods or benchmarks, emphasising any noteworthy changes or improvements.
- Compliance Highlights: Summarise compliance-related information, ensuring that all legal requirements are met and any potential issues are addressed.
- Employee Insights: Include information on employee trends, such as turnover rates, overtime patterns, or leave utilisation, offering insights into workforce dynamics.
- Budget vs. Actual Analysis: If applicable, compare actual payroll expenses to the budget, explaining any variations and outlining plans for adjustments if necessary.
- Recommendations: Conclude with any recommendations or action items based on the analysis, such as process improvements, cost-saving measures, or adjustments to benefit programs. Presenting the payroll report in a well-organised and informative manner allows HR professionals to effectively communicate the financial health of the workforce to their superiors.
Get A Free OpensoftHR Payroll Software Demo
I hope that this article has been useful for you in understanding more about Payroll reporting in Singapore. The downside about doing Payroll Reporting is that it can be very time-consuming if you create them manually. Good news is that with OpensoftHR Payroll Software, you can automate your entire Payroll Reporting Process – from your yearly payroll reports, to your monthly reports and even your itemised payslip. Reach out to us for a free demo to find out more.
 Home
Home